September 2023
Candida auris: an emerging multi-resistant fungus
Introduction Candida auris is a pathogen that has emerged as a global threat in recent years. It is the first human pathogenic fungus subject to international health alerts. The reason behind these concerns are – Public Health England reported in 2017 that almost all the C auris in the UK are fluconazole-resistant. There is also […]
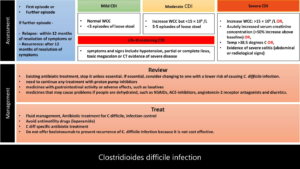
C difficile Infection guideline – comparison between NICE 2021 and IDSA 2021
What does NICE guideline 2021 say about assessing and managing C difficile infection? Comparison between NICE 2021 guideline and IDSA 2021 update IDSA/SHEA focussed update 2021 NICE 2021 1st episode of CDAD -1st line Fidaxomicin 200 mg BO PO 10 days Vancomycin 125 mg QDS PO 10 days 1st episode of CDAD - 2nd line […]
Brucella
Bacteria There are many Brucella species – not all known to cause human disease. Those known to cause human disease are – B melitensis, B abortus, B suis, B canis and B ceti. Brucella infection is a zoonosis – each Brucella sp is associated with some animal host – Brucella survives in the environment for […]
Aspergillus niger
The Fungus: Identification: It initially forms white colonies with a yellow back, which quickly becomes black. Conidia is rough, brownish-black, biseriate, and covers the entire vesicle. A key feature in diagnosing A. niger infection is the presence of calcium oxalate crystals on pathological examination. The presence of crystals can be taken as an indication of A niger […]
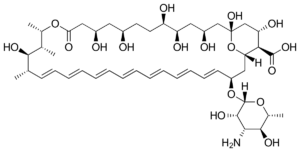
Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is a polyene antibiotic discovered in 1953 from the bacteria Streptomyces nodosus, in the Orinoco basin in Venezuela. Its name is derived from its amphoteric property, being able to react to both acid and base. It is insoluble at normal pH; hence it is available as a buffered colloidal solution, with sodium deoxycholate […]
Antibiotic – intrinsic resistance
Enterobacterales & Aeromonas Enterobacterales and Aeromonas are intrinsically resistant to benzylpenicillin, glycopeptides, lipoglycopeptides, fusidic acid, macrolides (Except Azithromycin, effective for typhoid/paratyphoid fever and erythromycin for travellers’ diarrhoea), lincosamides, streptogramins, rifampicin, and oxazolidinones. Bacteria Beta-lactams Non-beta-lactams Klebsiella pneumonia complex,Klebsiella oxytocaRoultella sp.Citrobacter koseri,Citrobacter amalonaticus Amoxicillin, Ticarcillin Klebsiella aerogenes,Enterobacter cloacae complexCitrobacter freundiiHafnia alvei Amoxicillin, Coamoxiclav,1st generation cephalosporinsCefoxitin Serratia […]
Aerococcus urinae
Aerococcus genus, a firmicute, was first identified in 1953 [Williams, 1953]. Multiple species have been identified since then; not all are human pathogens. Human pathogen Aerococcus viridans, Aerococcus urinae, Aerococcus urinae hominis,Aerococcus christensenii, (2001), Aerococcus sanguinicola. Not human pathogen Aerococcus urinae equi ( or Pediococcus urinae equi), Aerococcus suis, Aerococcus vaginalis. Laboratory identification: Aerococcus is a gram-positive coccus in clusters (like Staphylococcus), alpha-hemolytic on […]
Aeromonas spp.
Aeromonas are Gram-negative bacilli, widely distributed in nature, especially aquatic environments – freshwater, brackish water, sewage system, hospital water system, and even drinking water. It can also be found in food and domestic or farm animals. The Aeromonas genus consists of more than 30 species based on DNA-DNA hybridisation and 16S rDNA relatedness. Of these 30 […]
Adenovirus
Introduction For high-resolution images, scroll to the bottom of the page Human adenovirus has 7 species based on their haemagglutination character.Each species was divided into serotypes based on neutralisation (e.g. A- 12,18, 31). At present, genotyping is being used to classify Adenovirus.Different species of human adenovirus have different tissue tropism. Species Tissue tropism A GI, respiratory, […]